SO_DYFAMED Time Series - 1991-> ...
JC. MARTY : Head of mission and Project Leader
Head of logistic : J.
CHIAVERINI (B. AVRIL (-1993))
Cruise organisation : A.
STOCK
 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
GENERAL DESCRIPTION 
 LE
SERVICE D’OBSERVATION DYFAMED
LE
SERVICE D’OBSERVATION DYFAMED
Les séries temporelles d’observation au site DYFAMED ont reçu le label de Service Scientifique d’Observation de l’INSU en Janvier 1995. En fait, les observations régulières réalisées dans la zone centrale de la Mer Ligure ont été initiées dans le cadre du programme JGOFS France dès 1988. D’autre part, la zone retenue a fait l’objet dans le passé de nombreuses études par les équipes de l’Observatoire de Villefranche sur mer. Ces observations historiques et les nouvelles informations obtenues dans le cadre de ce service d’observation vont constituer une base de données incomparable pour comprendre et modéliser les évolutions à long terme de l’environnement méditerranéen.
Les résultats d’un tel programme sont donc attendus à l’échelle de la décennie ou plus.
A l’instar des deux autres Séries à Long Terme
initiées par le programme JGOFS (BATS et HOTS),
les objectifs
plus spécifiques du Service d’Observation DYFAMED sont
définis dans l’optique JGOFS :
- variations saisonnières et interannuelles physiques chimiques et biologiques
- relations entre les processus biologiques et chimiques en réponse aux forçages physiques
- variabilité et impact des apports de matière depuis le continent par la voie atmosphérique sur l’océan (en particulier pour leurs effets sur la production)
- variabilité annuelle et interannuelle des processus biogéochimiques dans la couche de surface de l'océan (production, régénération)
- variabilité des flux verticaux émis sous forme particulaire et dissoute dans la colonne d'eau et au sédiment
- données sur les tendances à long terme de certaines propriétés sélectionnées (O2)
- cadre pour la mise au point (validation) de nouvelles techniques, ou pour l’étude de processus spécifiques
Le service d’observation DYFAMED est très intimement lié à l’opération DYFAMED du programme PROOF (ex JGOFS-France). Les autres volets d’activités qui sont développés dans le cadre du programme PROOF (ex Programme France-Jgofs) sont :
1- les processus haute fréquence : campagne DYNAPROC (responsable V. Andersen), étude de la dynamique des processus rapides dans la colonne d’eau en période de production phytoplanctonique élevée. fréquence en période oligotrophe fait l’objet de la participation à PROSOPE. L’étude multidisciplinaire de la situation hivernale au cours de laquelle coexistent les mélanges verticaux intenses et des périodes de stabilisation suffisamment longues pour permettre des événements intenses mais brefs de production est proposée à l’horizon 2002.
2- l’approche pluriannuelle : A coté de l’opération DYNAPROC basée sur le schéma classique d’approche multidisciplinaire pour une période spécifique, l’étude pluriannuelle est poursuivie par les divers groupes poursuivant leur étude coordonnée.
 DYFAMED
PROGRAM
DYFAMED
PROGRAM
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
In
the framework of the France-JGOFS program, a long-term time-series
investigation (DYFAMED: Dynamics of Atmospheric Fluxes in the
MEDiterranean sea) has been undertaken in 1988 in the north-western
Mediterranean Sea. The "DYFAMED" site was first equipped with
sediment trap moorings and visited punctually for hydrological monitoring.
Atmospheric deposition survey was at the same time initiated in 1988 at the
Cape Ferrat station. Since 1991, monthly cruises have been conducted and
most of the JGOFS core parameters recorded.
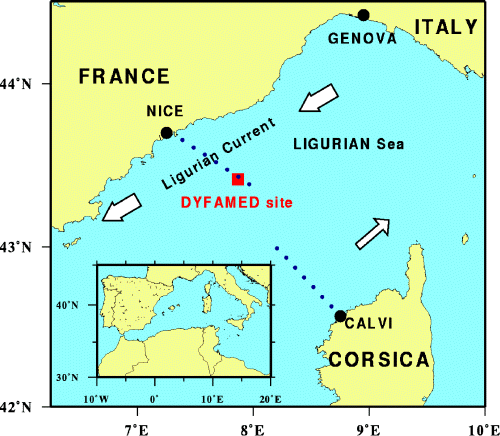
Location: The primary station is located at 43°25’N, 7°52’E in the north western sector of the Mediterranean Sea (Ligurian Sea) approximately 45 km south of Cape Ferrat, France, in 2,350 m of water. The central part of the western basin of the Mediterranean Sea constitutes a homogenous system isolated from direct coastal inputs by rivers but receive significant atmospheric input from deserts of the North Africa and from the industrialized countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea.
At this site, the seasonal succession of hydrological conditions induces production systems varying from mesotrophy in spring to oligotrophy in summer and fall.
The objectives of the DYFAMED program are as follow:
(1) to study the variations of hydrology and biogeochemistry at the seasonal and interannual scale (2) to investigate the ecosystem response to atmospheric deposition events and to long-term environmental/climate forcing, (3) to investigate and understand the ecological effects of meteorological forcing, especially the transition in community structure between spring mesotrophy and summer oligotrophy and (4) to estimate the air-to-sea exchange of carbon dioxide.
The DYFAMED program has been built around three types of actions (see synoptic table of activities and data):
-
1 Time-series core parameters measurements (monthly cruises since 1991)
-
2 Other time-series measurements (time series during a limited time)
-
3 Process studies (specific objectives multidisciplinary cruises)
1
Core measurements :
DYFAMED Observatory
Inauguration
and present status:
Field sampling began in 1986, pre-JGOFS, with a sediment trap mooring
and atmospheric deposition survey that were enhanced with a ship-based
biogeochemistry measurement program and benthic survey in 1991 that have
continued to the present. [References:
Oceanis, 25-2, 1999; Deep Sea Research Part II, vol. 49 (11), 2002]
Sampling
frequency and methods:
Approximately monthly field observations are conducted using the
French R/V Téthys II which is operated by the Centre National de la
Recherche Scientifique (CNRS) Institut National des Sciences de l’Univers
(INSU) and home-ported in Marseilles (France). The interdisciplinary station
work includes physical, chemical and biological observations and rate
measurements (see Table). In March 1999, a meteorological buoy was deployed
with plans to add in water optical and biogeochemical sensors in the near
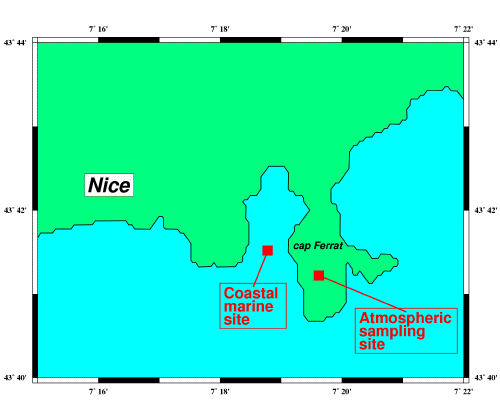
future. Atmospheric observations are conducted from the Cap Ferrat signal
station, situated on the southeastern coast of France (43° 41’ N, 7°
19’ 30’’ E; altitude 130 m).
Logistical
management and funding sources:
DYFAMED is maintained by scientist of the Laboratoire d’Océanographie de
Villefranche (Observatoire Océanologique de Villefranche) and of IAEA
Marine Environmental Laboratory in Monaco (for sediment trap experiments).
Funding is provided by INSU/CNRS.
Scientific Responsible : J.C. Marty (marty@obs-vlfr.fr), Laboratoire d’Océanographie de Villefranche, Université P. et M. Curie – CNRS – INSU, Observatoire Océanologique de Villefranche-sur-Mer, France.
2
Other time-series activities :
DYFAMED-JGOFS France program)
In
the frame of the JGOFS France program, a number of projects were (and are)
realized at the DYFAMED site with the aim of studying the seasonal
variations (during at least one year) of various processes using chemical
and biological approaches. These studies are realized in the course of the
monthly cruises of the DYFAMED Observatory, and the set of data is described
in the Table.
3
Process studies (DYFAMED-JGOFS France)
Other
multidisciplinary projects have
been realized in the course of JGOFS France at the DYFAMED site. They were
based on the study of a specific process at scales which cannot be achieved
through monthly cruises:
DYNAPROC
(P.I. V. Andersen) Dynamics of rapid processes controlling vertical flux
(one month at the DYFAMED site in May 95)
MIGZOO
(P.I. V. Andersen): Vertical migration of zooplankton
EIMETO
(P.I. C. Jeandel) : Exchanges between dissolved and particulate matter and
transfers
DYFABAC
(P.I. A. Bianchi): Deep bacterial activities using hyperbare sampler.
New
projects will be developed from 2003 at the DYFAMED site
in the course of the PROOF program (Processus
biogéochimiques dans l'océan et flux"):
PECHE (P.I. V. Andersen) : Production et Exportation du Carbone : contrôle par les organismes HEtérotrophes à petite échelle de temps
BARMED (P.I. C. Jeandel) Processus de synthèse et réactivité de la barytine dans les eaux de surface, dans la zone mésopélagique (twighlight zone) et à l’interface eau-sédiment
MELISSA (P.I. C. Migon) MEditerranée LImitationS Saisonnières
ACTION
(P.I. C. Goyet) Anthropogenic Carbon: Temporal Increase,
Observations and Numerization
LOCATION
![]() L’originalité du site
d’observation DYFAMED tient essentiellement à sa situation
dans la zone centrale de la Mer Ligure.
L’originalité du site
d’observation DYFAMED tient essentiellement à sa situation
dans la zone centrale de la Mer Ligure.
Ce site est placé dans la zone
centrale de la mer Ligure à environ 50 km de Nice sur la radiale
Nice Calvi.
La mer Ligure est caractérisée par trois
zones:
- Une bande côtière alimentée par le courant liguro-provençal et soumise à quelques apports continentaux, peu productive.
- La limite du courant Ligure et de la zone du large constitue la zone frontale qui bénéficie d'un enrichissement permanent en sels nutritifs en raison de la circulation secondaire associée au jet (objet de l'étude par le programme Frontal).
- Ce front isole complètement la zone du large (ou est situé le site DYFAMED), et pour laquelle la production primaire dépend des apports profonds de sel nutritifs mais aussi, pour une part encore mal déterminée, d'apports atmosphériques aussi bien pour l'azote (en période estivale) que pour certains métaux traces.
Le suivi du dépôt atmosphérique est donc une condition indispensable à la compréhension des processus de production en particulier pendant les périodes de stratification quand les sels nutritifs sont épuisés en surface (il est réalisé au sémaphore du Cap Ferrat). Dans cette zone, les cycles biogéochimiques dans la colonne d'eau et la vie benthique dépendent donc des flux verticaux passifs ou actifs (rôle du zooplancton), le transfert vertical étant très rapide lors d'épisodes brefs mais intenses (floraison printanière, pluies sahariennes).
Cette zone peut donc être considérée comme :
une zone de référence d'eaux oligotrophes à mesotrophes sans influence
marquée des eaux continentales et donc représentative de larges zones de l'océan mondial. L'observation peut donc se limiter à la seule dimension verticale, d'où la possibilité d'obtenir des informations à l'échelle globale à partir d'un seul site d'observation, et la possibilité d’utiliser les modèles 1D.
 SCIENTIFIC AREA
SCIENTIFIC AREA
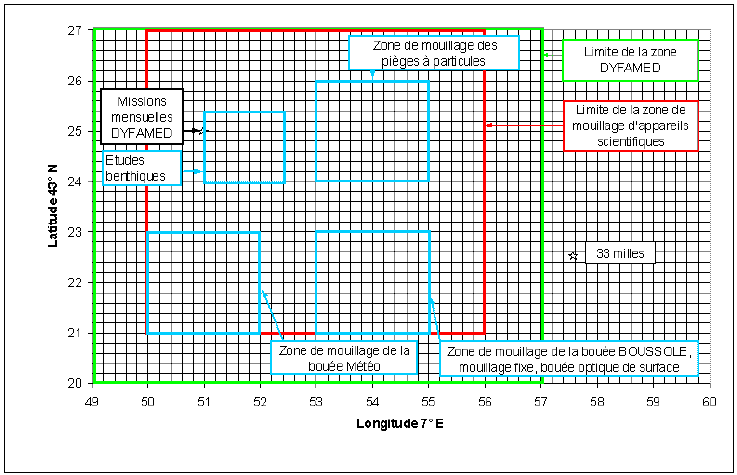
Le site DYFAMED, espace de travaux scientifiques en Mer Ligure, a été défini à la suite d’une réunion tenue le 16/10/98 à la Préfecture Maritime de Toulon. Cette zone couvre une surface de 7 milles sur 8 milles soit environ 19 0 km², elle est répertoriée sur les cartes marines depuis1999.
Si vous devez entreprendre une nouvelle activité dans ce secteur, vous devez impérativement en avertir à l'avance JC Marty (ou J. Chiavérini) de façon qu’il puisse effectuer toute démarche nécessaire auprès de la Préfecture Maritime et auprès des utilisateurs définis de cette zone.
ATMOSPHERIC LOCATION
FRANCE_NICE_sémaphore du Cap Ferrat.
![]() Le
site du Cap Ferrat constitue une avancée vers la mer (les
précipitations y sont plus faibles de 10% qu'au niveau de
l'aéroport de Nice), au milieu d'une zone littorale fortement
urbanisée.
Le
site du Cap Ferrat constitue une avancée vers la mer (les
précipitations y sont plus faibles de 10% qu'au niveau de
l'aéroport de Nice), au milieu d'une zone littorale fortement
urbanisée.
Cela signifie que ce site est à la fois protégé des apports locaux (grosses particules destinées à sédimenter très rapidement) et représentatif de la côte ligure nord, responsable d'apports anthropiques importants vers la Méditerranée occidentale, transportés à moyenne et grande distance. De nombreuses comparaisons entre les échantillons atmosphériques du Cap Ferrat et ceux prélevés au cours de campagnes océanographiques ou sur d'autres sites côtiers ouest-méditerranéens ont clairement démontré que les échantillons du Cap Ferrat reflètent tout-à-fait la composition chimique des aérosols et des précipitations de la Méditerranée nord-occidentale, et à plus forte raison de la Mer Ligure.
Ceci a été établi à travers plusieurs publications de rang international. Les trajectographies des masses d'air fournies par Météo-France (qui remontent jusqu'à trois jours avant la date donnée) sont disponibles quotidiennement aussi bien pour le Cap Ferrat que le site DYFAMED. Il apparaît que les masses d'air qui affectent les deux sites ont presque toujours la même origine et voyagent aux même niveaux de pression, ce qui justifie le choix du Cap Ferrat dans l'optique d'un couplage site côtier-site marin, pour une étude de la réponse marine aux apports atmosphériques.